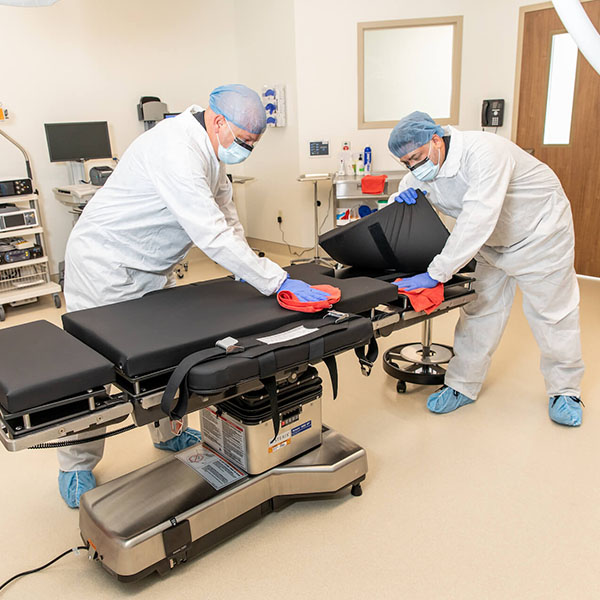
What are Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)?
- Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are infections that are acquired while receiving medical care. They can be caused by a variety of sources such as bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses, and can range from minor skin or bloodstream infections to life-threatening illnesses such as pneumonia or blood poisoning. These types of infections can occur in any healthcare setting, including hospitals, nursing homes and long-term care facilities.
Importance of reducing Healthcare Associated Infection in ambulatory surgical centers
- Reducing the prevalence of HAIs is an important goal for healthcare organizations. Effective prevention strategies include reducing cross-contamination by hand hygiene, proper cleaning and disinfection of medical instruments and surfaces, using personal protective equipment and following current infection control guidelines. Additionally, healthcare personnel must be educated and trained on the latest protocols to ensure that they are well-equipped to reduce the spread of infection.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that healthcare organizations track HAI data in order to identify areas of improvement. This data can then be used to develop targeted interventions and improve patient safety.
Establishing a comprehensive infection control program is the best way to reduce the prevalence of healthcare-associated infections and ensure that all patients receive quality care. Implementing these strategies can help protect the health of both staff and patients, while reducing hospital costs associated with treating HAIs.
Types of Hospital Associated Infections commonly found in ambulatory surgical centers
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs) are a major public health concern, especially those occurring in ambulatory surgical centers. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites and may cause serious illness or even death. Below is an overview of the types of HAIs commonly found in ambulatory surgical centers, as well as prevention strategies to reduce their prevalence.
- Surgical site infections
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are infections that occur after a surgical procedure in the part of the body where the surgery took place. These infections can be superficial, affecting the skin and subcutaneous tissue, or more serious, involving deeper tissues or organs. SSIs can develop within a few days or even months after surgery, and they can range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Risk factors for SSIs include having a weakened immune system, being older in age, and having a longer or more complex surgical procedure. Symptoms of an SSI can include redness, swelling, and pain at the surgical site, as well as fever and drainage from the site. SSIs can be treated with antibiotics, but in severe cases, additional surgery may be needed. It is important to take steps to prevent SSIs by following proper infection control protocols during surgery and aftercare.
- Urinary tract infections
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most common types of healthcare-associated infections. UTIs can affect any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. UTIs are often caused by bacteria entering the urinary system through the urethra, and they can be more common in individuals with catheters, who have impaired immune systems, or who are hospitalized for other medical conditions. Symptoms of a UTI can include a frequent urge to urinate, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and abdominal pain. UTIs can be treated with antibiotics, but they can lead to more serious complications if left untreated. It is important for healthcare facilities to follow proper infection control protocols to prevent the spread of UTIs.
- Bloodstream infections
A healthcare-associated bloodstream infection (BSI) is an infection that occurs when bacteria or other pathogens enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. BSIs can occur in a hospital or other healthcare setting, and they can be caused by a variety of factors, including the use of medical devices, such as catheters, and the presence of other infections or medical conditions. Symptoms of a BSI can include fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and low blood pressure. BSIs can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, and they can lead to serious complications, such as organ damage. It is important for healthcare facilities to follow proper infection control protocols, such as proper hand hygiene and sterilization of equipment, to prevent the spread of BSIs.
Steps to improve patient safety by reducing HAIs in ambulatory surgical centers
- Adhering to proper hand hygiene protocols
- Proper hand hygiene is essential to reducing the spread of Health care-Associated Infections (HAIs). Healthcare workers should wash their hands before and after patient contact, as well as any time they may have come into contact with a contaminated surface or object. The proper hand washing technique requires using soap and warm water and scrubbing for at least 20 seconds. Healthcare workers should also dry their hands with a single-use paper towel and use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer to help reduce the spread of infection. Proper hand hygiene is essential for healthcare workers in order to protect both themselves and their patients from HAIs.
- Sterilization and disinfection of equipment
- Sterilization and disinfection of equipment are important steps in preventing the spread of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in ambulatory surgical centers. Sterilization is the process of destroying all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, on a surface or instrument. This is typically done using heat, chemicals, or radiation. Disinfection is the process of destroying or inactivating most forms of infectious agents on a surface or instrument, but it does not necessarily kill all microorganisms. There are different levels of disinfection, and the appropriate level should be chosen based on the type of equipment and the risk of infection transmission. Proper sterilization and disinfection of equipment are essential to preventing the spread of HAIs and protecting patient safety. It is important for ambulatory surgical centers to have clear protocols in place for cleaning and sterilizing equipment and to ensure that all staff are trained in the proper use of these protocols.
- Use of personal protective equipment
- The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is an important part of reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in ambulatory surgical centers. PPE refers to clothing, gloves, masks, and other equipment that is worn to protect healthcare workers and patients from the transmission of infectious agents. PPE can help to prevent the spread of HAIs by creating a physical barrier between the healthcare worker and the patient. This is especially important in surgical settings, where there is a higher risk of infection due to the presence of open wounds and the use of invasive medical devices. PPE should be used according to the recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other professional organizations. It is important for ambulatory surgical centers to have a supply of PPE on hand and to ensure that all staff are trained in the proper use of PPE to reduce the risk of HAIs.
- Patient education on preventing infections
- Patient education can play a key role in reducing healthcare-associated infections in surgical ambulatory centers. By providing patients with information about the importance of proper hand hygiene, wound care, and other infection prevention measures, they can take an active role in preventing the spread of infections. This can be particularly effective in ambulatory surgical centers, where patients may be more likely to come into contact with other people or surfaces that could potentially harbor germs. Additionally, educating patients about the signs and symptoms of infections and encouraging them to report any concerns to their healthcare providers can help to identify and treat infections early on, which can help to prevent their spread. Overall, patient education is an important component of infection prevention efforts in surgical ambulatory centers and can contribute to a safer and more effective healthcare environment.
Healthcare Environmental Services (EVS) and Best practices for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers
- Improve EVS (Environmental Services)
Improved environmental services, or EVS, in a healthcare setting, such as an ambulatory surgical center, can help to reduce the occurrence of healthcare associated infections (HAIs). HAIs are infections that patients acquire while receiving treatment for another condition in a healthcare facility. These infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor hand hygiene, contaminated equipment, and inadequate cleaning of the environment.
Implementing better EVS practices, such as more frequent cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, proper sterilization and storage of equipment, and adequate ventilation, can all help to reduce the risk of HAIs. These practices create a cleaner and safer environment for both patients and healthcare workers, and can ultimately lead to better patient safety. Studies have shown that implementing improved EVS practices can significantly reduce the rates of HAIs in a healthcare setting, and can lead to healthcare cost savings for the facility.
- Implementing a thorough cleaning and disinfection program
- One of the best practices for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers is to implement a thorough cleaning and disinfection program. This should involve regularly cleaning and disinfecting all surfaces, equipment, and instruments in the facility, using appropriate cleaning and disinfecting agents. It may also be necessary to use special cleaning and disinfection procedures for certain types of equipment or in areas where the risk of infection is higher. Additionally, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, can help to reduce the risk of transmission of infections from person to person. Other best practices for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers may include implementing hand hygiene protocols, properly handling and disposing of hazardous materials, and following recommended guidelines for sterilization and disinfection. By following these best practices, ambulatory surgical centers can help to protect patients and healthcare workers from the risk of healthcare-associated infection.
- Ensuring proper sterilization of instruments
- Ensuring proper sterilization of instruments is an essential best practice for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers. Sterilization is the process of eliminating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, from instruments and surfaces. There are several methods for sterilizing instruments, including heat, chemical, and radiation methods. It is important to choose the appropriate sterilization method based on the type of instrument being sterilized, as different materials may be more or less resistant to certain methods. In addition to selecting the appropriate sterilization method, it is also important to follow proper sterilization protocols, including proper handling and packaging of instruments, monitoring sterilization cycles, and regularly checking sterilization equipment to ensure it is functioning properly. By following these best practices, ambulatory surgical centers can help to ensure that instruments are properly sterilized and free of any potential pathogens, helping to reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
- Developing protocols for handling and disposing of contaminated materials
- Developing protocols for handling and disposing of contaminated materials is another key best practice for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers. Contaminated materials, such as dressings, bandages, and other waste products, can harbor harmful microorganisms that can cause infections if they come into contact with patients or healthcare workers. To reduce the risk of infections, it is important to have clear protocols in place for handling and disposing of contaminated materials. These protocols should outline the appropriate steps for segregating and properly labeling contaminated materials, as well as the proper methods for disposing of them in a way that minimizes the risk of exposure to harmful microorganisms. It may also be necessary to use special handling and disposal procedures for certain types of contaminated materials, such as sharps or hazardous chemicals. By developing and following these protocols, ambulatory surgical centers can help to ensure that contaminated materials are properly handled and disposed of, helping to reduce the risk of infections.
- Collaborating with healthcare professionals and organizations to stay up-to-date on the latest infection control guidelines
- Collaborating with healthcare professionals and organizations is another important best practice for infection control in ambulatory surgical centers. Staying up-to-date on the latest infection control guidelines and recommendations can help ambulatory surgical centers to identify and implement the most effective practices for preventing healthcare-associated infections. This may involve working with professional organizations, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO), or with local health departments or infection control committees. It may also involve participating in continuing education opportunities or attending conferences and workshops on infection control. By staying informed and engaged with the broader healthcare community, ambulatory surgical centers can ensure that they are adopting the most current and effective infection control practices, helping to protect patients and healthcare workers from the risk of infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ambulatory surgical centers can help to reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections by following best practices for infection control, including proper sterilization procedures, developing protocols for handling and disposing of contaminated materials, and collaborating with healthcare professionals and organizations to stay up-to-date on the latest guidelines. By taking these proactive steps to reduce the risk of infection, ambulatory surgical centers can help to protect patients and healthcare workers from the potential dangers associated with healthcare associated infections.